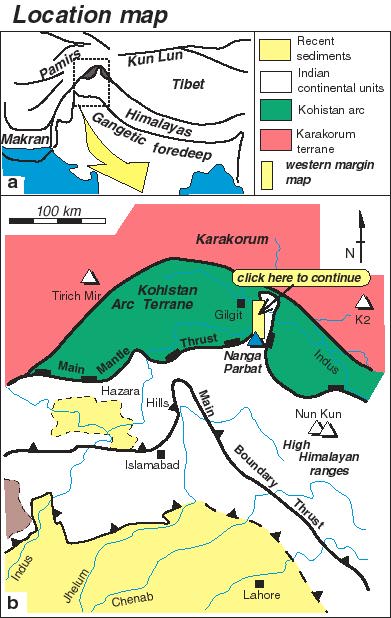

The mountain of Nanga Parbat is the westernmost 8000m peak of the Himalayan chain. Geologically the mountain gives its name to a massif of rocks derived from the Indian continent. These rocks were originally thrust beneath the over-riding Kohistan island arc terrane (the southern margin of the Asian landmass prior to India-Asia collision). The Kohistan arc rims the Nanga Parbat massif on three sides. Early workers considered the massif to occupy the core of a north-south trending antiform. As a consequence of erosion through this antiform, today we can see levels within the collision belt that would otherwise be buried.
This web site provides a flavour of the geology of the Nanga Parbat massif, particularly its tectonic history. You can follow a virtual field excursion, examine the once deeply-buried continental crust in its heart, get additional information on the topography, exhumation and cooling history of the massif and a list of references to follow up.